
Product Introduction
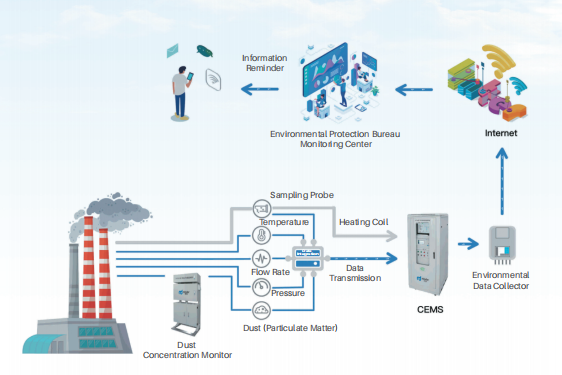
The Continuous Emission Monitoring System (CEMS) consists of four basic components: a gaseous pollutant monitoring subsystem, a particulate (dust) monitoring subsystem, a flue gas parameter monitoring subsystem, and a data acquisition and processing subsystem. It is capable of monitoring various parameters in the gas, including SO2, NOx, O2, particulate matter, temperature, pressure, flow rate, and humidity.
Get a quoteMain Features
The gas analyzer uses a xenon lamp as the light source, with a lifespan of up to 10 years.
The gas analyzer employs holographic grating spectroscopy and array sensing with no moving parts, ensuring high reliability.
The system automatically calibrates the instrument daily, enhancing data reliability.
Features automatic alarm and recording functions for anomalies such as faults, power outages, and exceeded detection data thresholds.
Easy maintenance with low upkeep costs.
The sampling probe uses a nickel-titanium alloy filter with a filtration precision of 5 microns, effectively removing particulates from the gas sample.
The control system enables automatic backflushing to minimize blockage issues and reduce maintenance requirements.
All control signals are managed through integrated circuits, simplifying system wiring and facilitating maintenance.
Preprocessing utilizes multistage particulate filtration technology to extend the lifespan of the gas chamber.
Equipped with a filtering buffer chamber, the water mist in the gas sample can be fully vaporized, preventing condensation and clumping, especially suited for high-humidity environments.
Target Customers
Suitable for various environmental monitoring units at all levels, including thermal power plants, industrial kilns, industrial boilers, steel sintering plants, steel mills, cement industry, waste incineration plants, and other applications requiring continuous monitoring of flue gas emissions.
Application
Applicable for the detection of emissions concentration and total emissions from fixed pollution sources, as well as the measurement of flue gas exhaust parameters (dynamic pressure, static pressure, temperature, flow rate, standard dry flow rate, etc.). It is also used for determining the flue gas oxygen content, air excess ratio, and measuring the concentration, calculated concentration, and total emissions of SO2 and NOx from various boilers and industrial furnaces.
